Introduction to SAP ABAP
SAP ABAP Programming
Hello everyone. In today's post, I will make an introduction to the ABAP programming language and prepare a blog series progressing from basic to advanced level. I hope the information I will reinforce with some theoretical knowledge and practices will be useful for those interested.
What is SAP ABAP?
ABAP (Advanced Business Application Programming) is a high-level software language used by SAP, a German software company, to develop ERP products. With ABAP programming, products containing financial accounting, material management, asset management and all other SAP modules are customized. It is quite easy to learn, has a syntax similar to SQL queries. Products are developed with standard or user-specific tables, data belonging to these tables and the use and processing of this data.
The ABAP development environment is SAP Logon, which is a licensed product. Systems are defined within SAP Logon and each system is divided into different systems within itself. Generally every company has 3 different systems. These are Dev-Development System, QA-Test System and PRD-Production System. These systems may vary depending on the company. Developments are made in the Dev system, developments made in the Test system are tested, and the product that will reach the end user is moved to the Production system. This transportation process is done through Requests . I will mention the process of getting a Request in the later parts of the article. Now let's continue with SAP Logon tools and how to make ABAP developments.
SAP LOGON SYSTEM DEFINITION
When we run SAP Logon, an empty screen will appear. We will define the system we will develop with the following steps. The interface appearance may vary depending on the version or theme.
1. First, we click New Item.
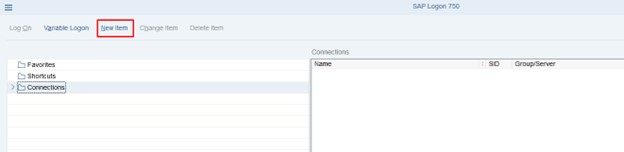
2. Then we continue by clicking next in the pop-up that opens.
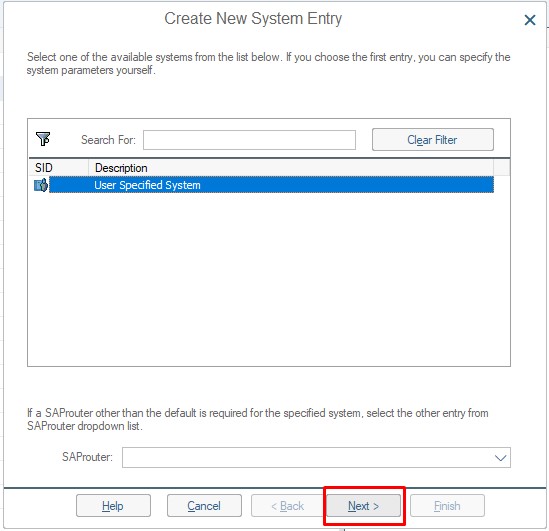
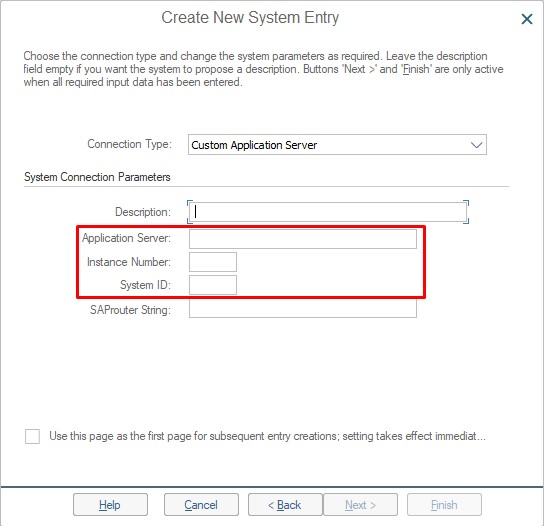
3. In the opened screen, fields where we will enter system information will appear. After filling these fields completely, we can click Finish.
SAP ABAP WORKBENCH
We can define ABAP Workbench as a set of tools that work in an integrated way with each other, contain all the tools to be used in developing a product, and enable the development of ABAP applications:
- ABAP Editor
- Data Dictionary
- Menu Painter
- Screen Painter
- Function Builder
- Debugger
- Object Navigator
There is a different Transaction Code for each tool. With these T-Codes, we can go to the tool we want to use and start developing applications. Before moving on to programming, let's see some important tools.
DATA DICTIONARY
We can go to Data Dictionary by typing the SE11 T-Code in the field in the upper left corner.
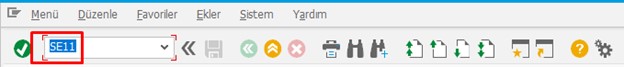
Then the screen that will appear is as follows:
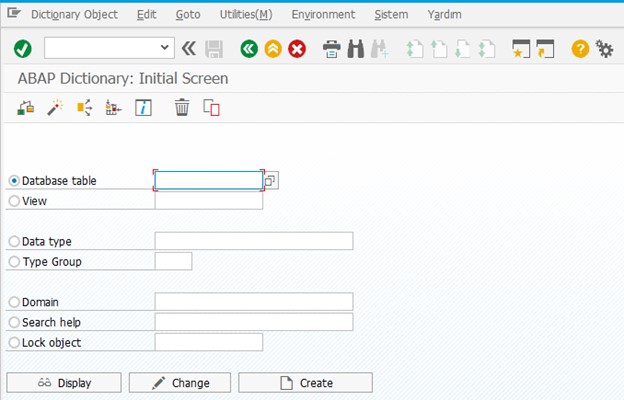
As we can see here, there are some tools under the name Data Dictionary. The tools shown here are used to develop an application. The most important and frequently used ones are Database Table and Data Type. These tools consist of standard or custom objects. SAP has some standard objects. The easiest way to distinguish them is the naming standard. Because the objects we create start with Z when named. We can consider namings that do not start with Z as SAP's standard objects.
OBJECT NAVIGATOR
We go to Object Navigator with SE80 T-Code.

As we can see on the left side, there are objects.
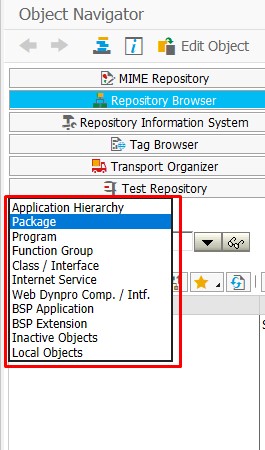
If we want to view or create new objects found here, we can use the SE80 Object Navigator transaction.
ABAP EDITOR
We can access the editor where we will write ABAP codes with SE38 T-code.
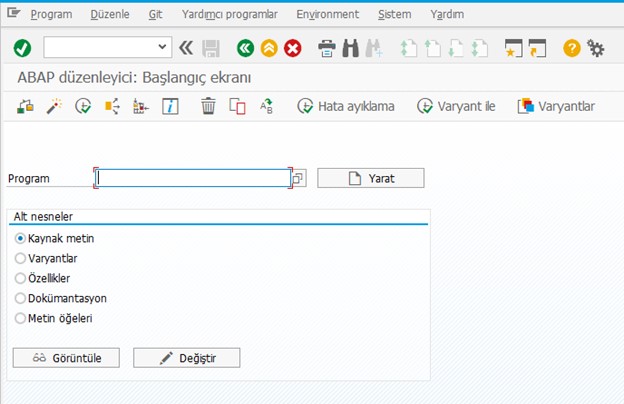
In the field we see here, we can view existing programs or create a new program.
In this article, I have shared the most basic information we need to know before starting ABAP programming. We will start programming in the next article.
← Back to TECHNOBLOG